Core Facilities News - July 2024 - ASU at SEMICON West

July 2024 Newsletter
Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.
ASU Microelectronics

Arizona State University is spearheading efforts to revive America’s microelectronics industry, crucial for national security and economic strength. ASU is working with industry and government entities to enhance domestic semiconductor manufacturing by expanding the talent pipeline through the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering. This initiative aligns with industry needs, as advised by ASU's Microelectronics Industry Council.
Our Economic Development and Corporate Engagement and Strategic Partnerships teams will be attending the upcoming SEMICON West conference to share how we are advancing semiconductor manufacturing capabilities in the US.
The SEMICON West Conference
SEMICON West is an important microelectronics event that brings the diverse global electronics supply chain together. At the convention, attendees will address the semiconductor ecosystem’s greatest opportunities and challenges through programs highlighting Market Intelligence, Standards, Sustainability, Workforce Development, Supply Chain Management and more. Photo courtesy SEMICON West Website
How SEMI member companies are creating a stronger world.
ASU at SEMICON West over the years
Over the last 20 years, ASU has attended SEMICON West to strengthen industry relationships, learn about new technologies and meet key personnel from partner organizations. They promote new research or inventions to attract clients to our Nanofabrication Cores. Attendees connect with equipment and materials vendors for lab expansion efforts, research technological trends and support the ASU booth. ASU staff find the conference rewarding and look forward to Phoenix hosting it in 2025.
ASU staff and faculty at SEMICON West 2023.
Teams work together to drive ASU's microelectronics initiatives
Southwest Advanced Prototyping (SWAP) Hub

Arizona State University leads the Southwest Advanced Prototyping (SWAP) Hub, one of eight regional innovation hubs under the Department of Defense’s Microelectronics Commons. Funded by a $39.8 million DoD investment, the SWAP Hub accelerates the development and production of critical microelectronics technologies. It aims to revitalize U.S. semiconductor manufacturing by focusing on transitioning research to production and building a skilled workforce.
How ASU is leading this DoD Microelectronics Commons Hub
Corporate Engagement and Strategic Partnerships
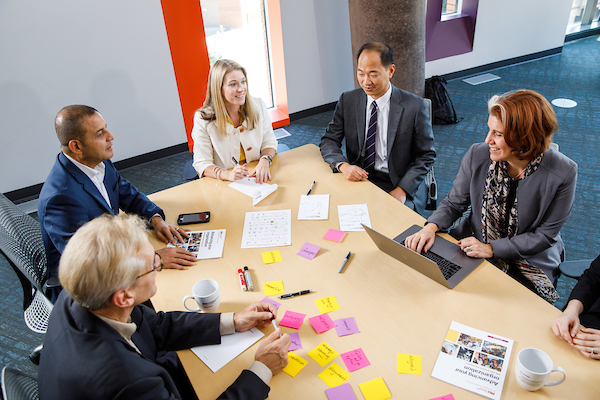

The Corporate Engagement and Strategic Partnerships team creates opportunities for individualized, transformative and impactful collaborations. From enhancing workplace diversity to advancing R&D initiatives, they help organizations achieve their goals. Grace O’Sullivan, VP of Corporate Engagement and Strategic Partnerships, says the "Corporate Innovation Labs offer unique collaboration opportunities for both ASU and industry partners, providing a testbed for rapid prototype and product development."
How corporate engagement is creating partnerships to drive innovation.
Economic Development
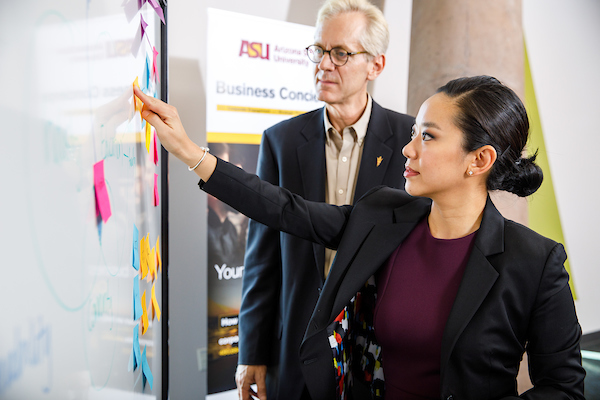

The ASU Economic Development team drives business attraction, retention and expansion strategies to boost the Greater Phoenix region's economy. Leveraging ASU's significant economic impact, they promote growth through initiatives like the semiconductor processing certificate, which provides strategic training and fosters industry partnerships in the microelectronics sector.
How Economic Development is helping industry grow.
ASU Core Research Facilities

The ASU Core Research Facilities offer advanced tools and expertise for device processing, characterization, development and fabrication across more than 45,000 square feet of clean room space. ASU NanoFab specializes in various electronics fields, providing state-of-the-art resources for research and industry partners. The Advanced Electronics and Photonics facility bridges the gap between innovation and product development, offering comprehensive electronics design, fabrication, testing and integration capabilities in a secure environment.
How Core Facilities are advancing semiconductor R&D.
This year at SEMICON West

The ASU team will have a booth at SEMICON West from July 9 – 11 at the Moscone Center in San Francisco, CA. Join them to explore groundbreaking technologies transforming the microelectronics sector and enabling smart applications. They will be at booth 5574 by the Beer and Wine Garden to talk about the Department of Defense Microelectronics Commons and the Southwest Advanced Prototyping (SWAP) Hub, among other ASU microelectronics and semiconductor industry resources.
SEMICON West 2024 information.
Core Facilities News - June 2024 - Instrument Design & Fabrication Staff Highlight
Core Research Facilities June 2024 Newsletter

June 2024 Newsletter
Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.
Instrument Design and Fabrication Core Employee Highlight
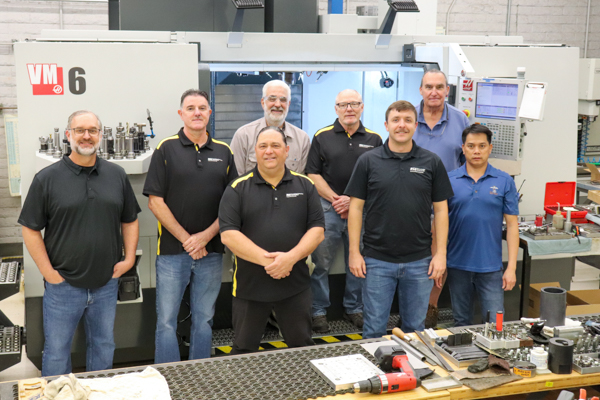

The Instrument Design and Fabrication (IDF) Facility offers a wide range of services for ASU researchers, peer institutions and private industry partners. With expert staff and capabilities from our Electronics and Machine Shops, we are ready to help you accomplish your project goals.
Meet the IDF Team
Brian Ipema, Director

Brian Ipema manages the the Machine and Electronics Shops as the IDF Core's Operations Director. With an engineering background in material analysis, design and manufacturing, his expertise lies in scientific research and development prototyping. Brian has supported diverse organizations, from Medtronic and Intel to the DoD. He is certified in SolidWorks, among other professional certifications.
James Makar, Machine Shop Manager

James "Jim" Makar joined ASU in 2004, leveraging his vast experience in the semiconductor, aerospace and robotics industries to manage the IDF Core's Machine Shop. Jim finds turning initial concepts into completed projects with researchers and faculty "tremendously rewarding."
Daniel Saine, P.E., Electronics Shop Manager
Daniel "Dan" Saine, a registered Professional Electrical Engineer, manages the Electronics Shop. He has experience in RF, digital and analog systems. Notable projects include the International Space Station's power system, the Army FIST communications system and the first CAT scan X-ray processor.
Gerald Lacy, Senior Instrument Maker and Designer

Gerald "Jerry" Lacy joined ASU in 2016 as a Senior Instrument Maker Designer specializing in machining, mechanical design and assembly. His work supports research on brain injury and virus characterization. He has contributed the CXFEL and various NASA projects. Certified in SolidWorks, he brings expertise from many industries.
Chris Bello, Machinist

Christopher "Chris" Bello joined the IDF Core in July 2023, with a rich background as a machinist specializing in aerospace and semiconductor parts. Chris brings expertise honed through a 6400-hour apprenticeship where he earned the title of Journeyman Machinist from the National Tooling & Machining Association and the Arizona Department of Labor.
Mark White, Instrument Maker

Mark White joined ASU as a Machinist/Instrument Maker in 2004, leveraging 45 years of experience across semiconductor, aerospace, tool and die and agricultural and mining equipment repair. He thrives on solving complex problems and meeting the diverse functional and material demands in ASU's dynamic setting.
"It is also rewarding being able to work with and learn from our customers since so many of them are degreed faculty in a variety of fields and disciplines which contributes to my overall understanding of the world we live in. - Mark White
Brian Smith, Instrument Maker
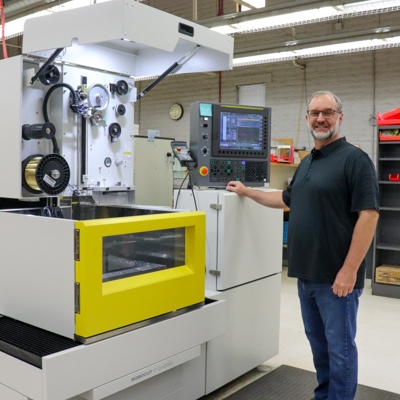

Brian Smith has been a machinist in the manufacturing industry for 25 years, with a focus on aerospace. Brian joined ASU Instrument Design and Fabrication Core in 2016 specializing in CAD modeling and enjoys collaborating with clients on their design projects.
Tan Nguyen, Senior Machinist
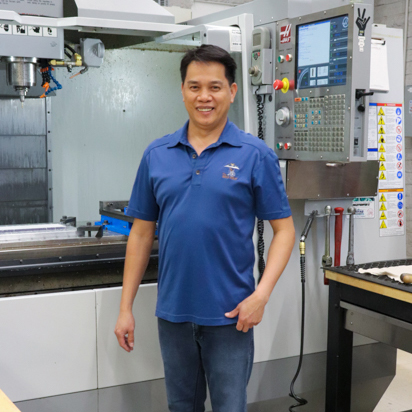

Tan Nguyen is a Senior Machinist for the IDF Core, briniging experience from the aerospace, defense and semiconductor industries. He specializes in sketching solid model parts, programming and preparing CNC machines to create essential components for research initiatives.
More about the team and their successes.
IDF News
IDF and the ASU Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences

Brian and Dan have been working with Dr. Yvonne Sawall from ASU BIOS on an NSF-funded project studying eddies in coral reefs. The BIO-RESORT is an instrument engineered to measure the metabolic rates or marine organisms in the field. Here, we can see them as they rebuild and update the CPU for the water sampling units crucial to the BIO-RESORT's functioning.
How the water sampling units support the BIO-RESORT.
Employees of the IDF Core are proud to have received an ISO 9001: 2015 and AS9100D certification

Compliance to ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100D requirements is the basis for organizing and operating our quality management system.
The IDF Core "has demonstrated its commitment to world class quality by implementing and becoming certified to the ISO 9001: 2015 and AS9100D standard. They have joined an elite number of organizations worldwide who have achieved certification to this globally recognized quality standard,” said Randy Daugharthy, Vice President – Registrar at the Performance Review Institute Registrar.
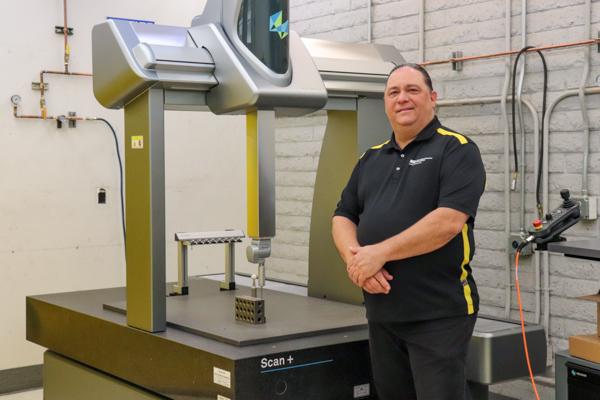
New Maching Shop Equipment
The Hexagon Scan+
A versatile 900 x 1200 x 800mm Coordinate Measuring Machine, designed for detailed assessments of size and form with superior tactile scanning capabilities.
Tactile scanning enables the Scan+ to collect numerous surface points rapidly, ensuring precise form and profile evaluations for various parts. This machine integrates tactile scanning with an adaptable automatic probe head, facilitating the examination of intricate components from multiple angles.
The integrated styli changer rack enhances efficiency, allowing swift transitions between styli configurations during measurements, all without compromising the measurement scope.
More Instrument Design and Fabrication Equipment.
Core Facilities News - April 2024 - Ultrafast Laser Highlight
Core Research Facilities April 2024 Newsletter

April 2024 Newsletter
Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.
Ultrafast Laser Facility

For this month's newsletter, we're going to focus on the people that make our Ultrafast Laser Facility, part of our larger Biosciences Core, so great!
The Ultrafast Laser (UFL) Facility leads in time-resolved laser spectroscopy, using cutting-edge femtosecond and picosecond pulsed lasers with spectroscopes and microscopes. This enables real-time kinetic measurements across various wavelengths for dynamic process characterization. We specialize in advanced laser technologies for chemical, biological and materials science research, offering high spatial resolution and sensitivity, including at the single-molecule level, to meet modern research needs.
Meet the UFL team
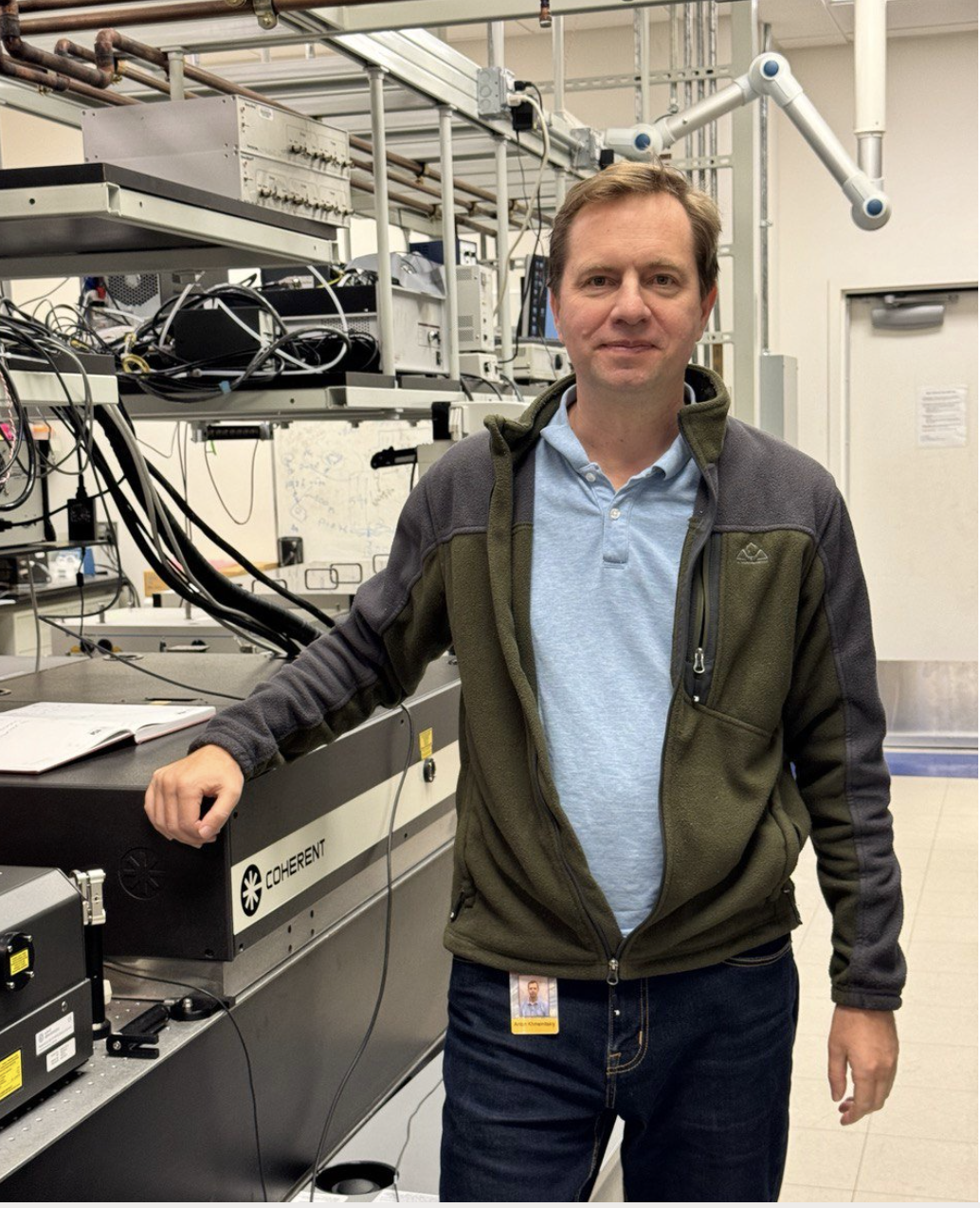

Anton Khmelnitskiy, a research professional and a manager of the UFL.
Anton's research investigates ultrafast dynamics of excitation energy transfer and charge separation in both natural and artificial systems. Anton is recognized as an expert in laser spectroscopy and experimental data analysis.
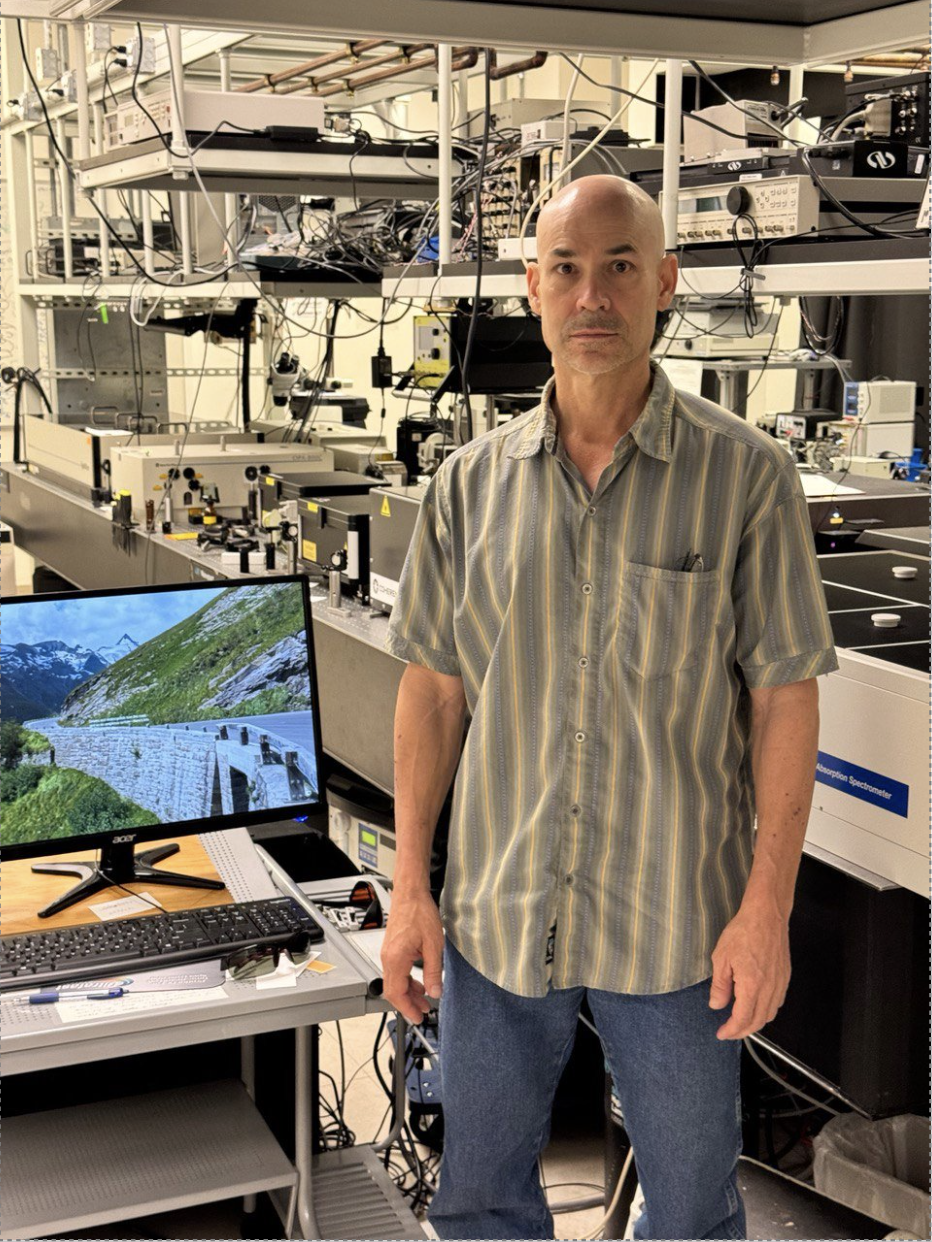

Doug Daniel is a manager in the UFL and also works in the Eyring Materials Center.
Doug's area of expertise is in Raman spectroscopy, powder x-ray diffraction, microscopy and time correlated single photon counting.
UFL's equipment
The Ultrafast Laser Facility acquired two new advanced laser setups at the end of 2023.
Astrella Lasers
Known for their reliability, user-friendly operation, and integrated design that combines the femtosecond oscillator and Ti:Sapphire amplifier together with pump lasers in a single unit. Astrella lasers are built with stability and precision in mind, offering consistent performance that is critical for research applications.
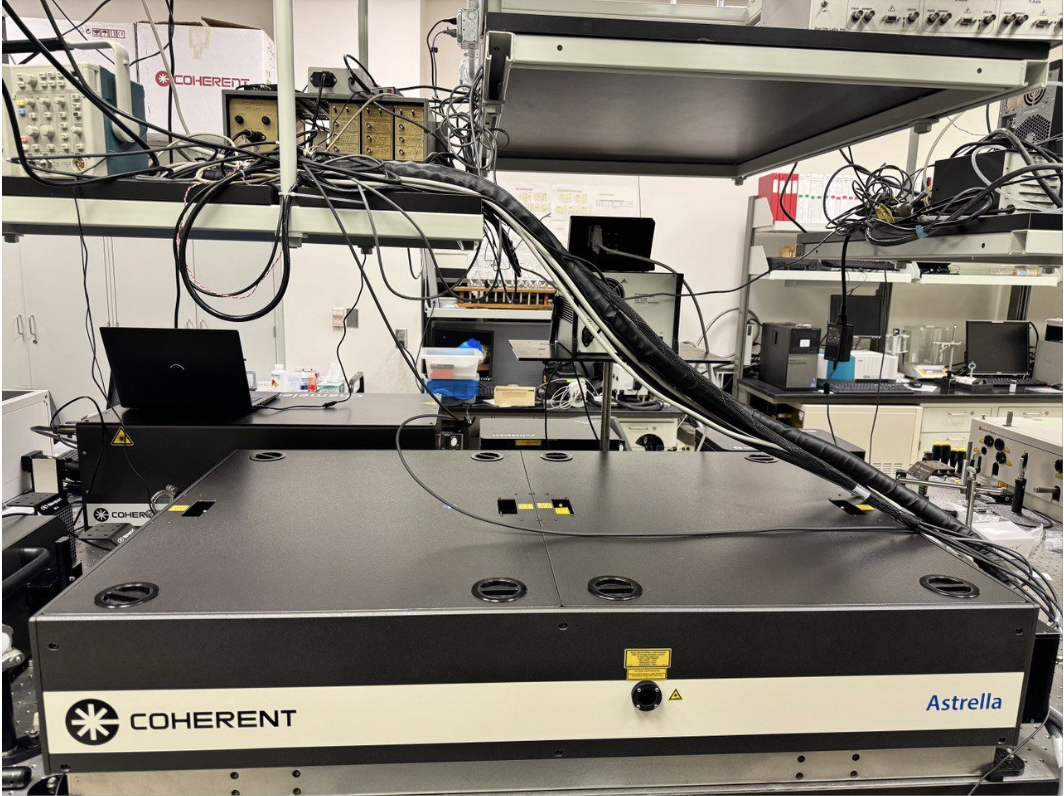

Astrella is coupled to Opera, an optical parametric amplifier from Coherent, which extends the wavelength range of these ultrafast pulses well beyond fixed 800 nm, which is required for pump-probe spectroscopy of various samples. As a result, this combination can produce femtosecond pulses at wavelengths from 240 nm (UV) up to 20,000 nm (IR) seamlessly.
Chameleon Discovery NX

The Discovery NX is an ultrafast tunable laser with a repetition rate of 80 MHz. It delivers the highest power to address needs of users of fluorescence microscopy, time correlated single photon counting and streak camera fluorescence measurements. Additional harmonic generation setup provides gap-free, automated tuning from 330 nm to 1320 nm and the PulsSelect module allows for decreasing the repetition rate to sub KHz.
Transient Absorption Spectroscopy |
Broadband Pump-Pulse Spectrometer |
UFL Supports Research
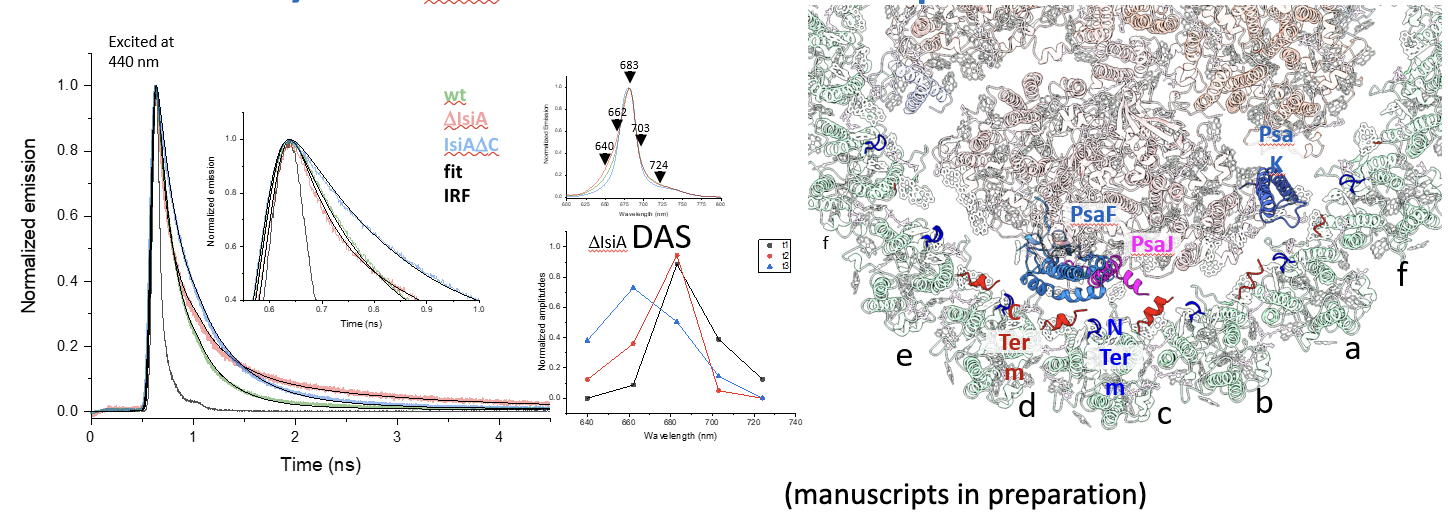
Mazor Lab
In the Mazor Lab, the team uses short-pulsed lasers to examine how the structure and function of membrane complexes are related in the process of oxygenic photosynthesis. Specifically, graduate student Jin Li from Dr. Yuval Mazor's group is conducting this research in partnership with the Ultrafast Laser Facility.
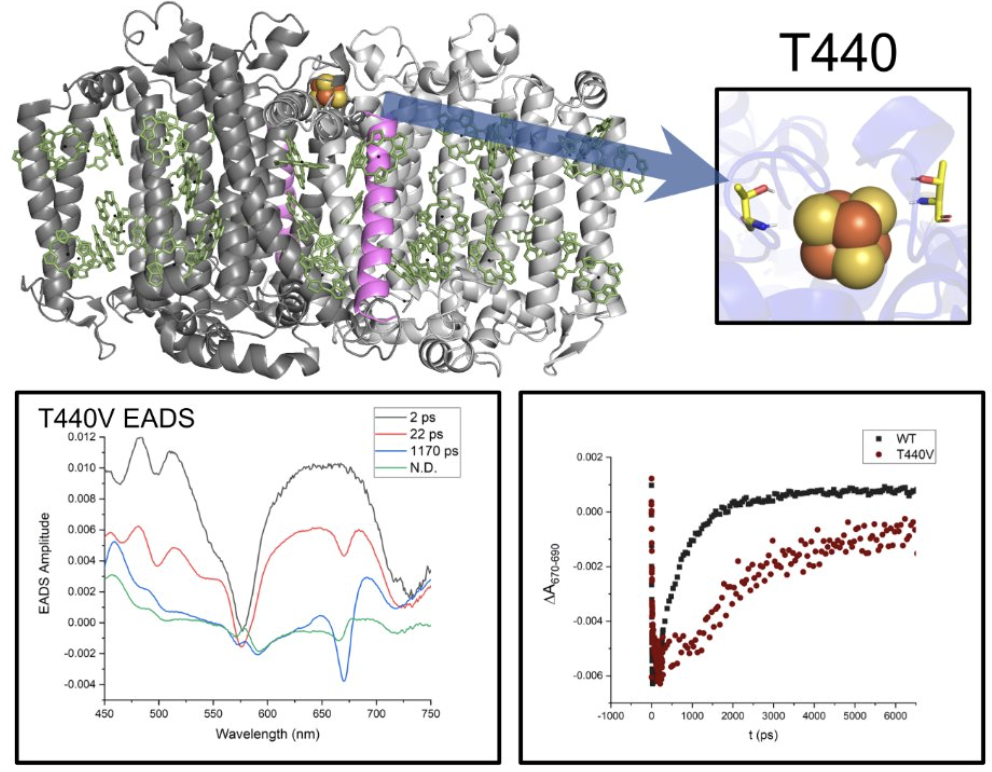
Redding Lab
In the Redding Lab, graduate student Jesse Granstrom, working under Dr. Kevin Redding, has employed the HELIOS ultrafast laser spectrometer and Astrella laser. This equipment was used to investigate the rate of electron transfer within the T440V mutant of the heliobacterial reaction center, a variant known for perturbations in its iron-sulfur (FeS) or FX cluster.
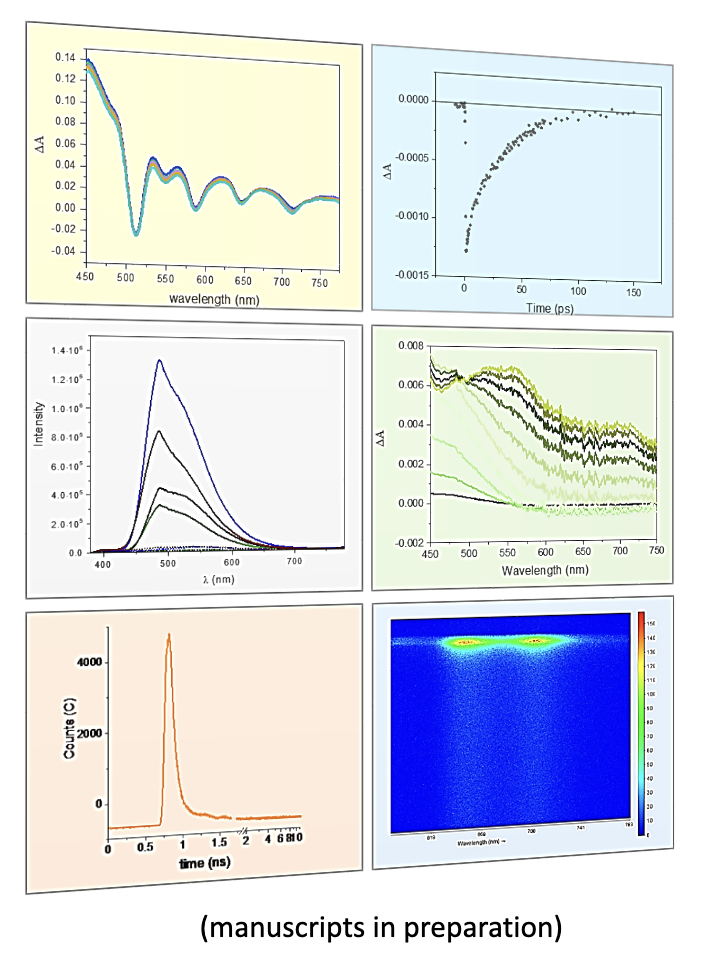
Moore Lab
The Moore Lab is leveraging transient absorption methods to investigate proton dynamics in hydrogen-bonded systems. Their work is centered on understanding how protons move in response to electron transfer.
Simultaneously, the team is examining the photonic behavior of porphyrin derivatives and the potential to boost photocatalytic reactions.
Research conducted by Emmanuel Odella, Rodrigo Dominguez and Edwin Gonzalez of the Tom and Ana Moore lab in collaboration with Ultrafast Laser Facility manager Anton Khmelnitskiy.
The impact of the Moore Lab's research.
Publications
The PshX subunit of the photochemical reaction center from Heliobacterium modesticaldum acts as a low-energy antenna
Dr. Su Lin, formerly of the Ultrafast Laser Facility at ASU Core Research Facilities, assisted with transient absorbance experiments in this research.
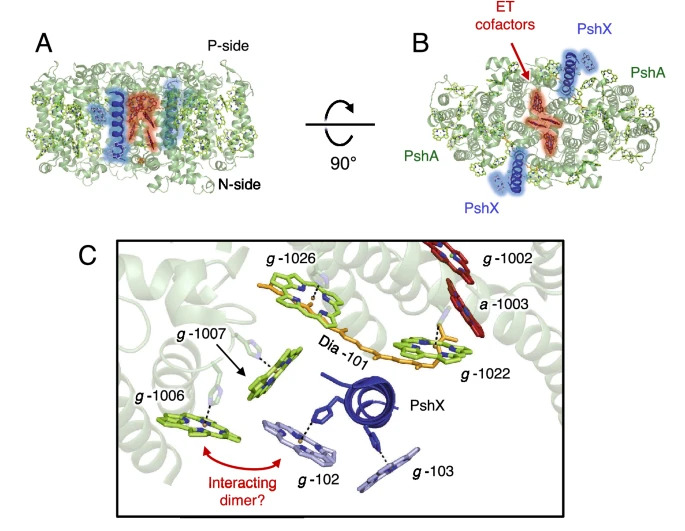
Abstract
Researchers discovered a new polypeptide, PshX, in Heliobacterium modesticaldum's photochemical center that binds bacteriochlorophyll g. Using CRISPR-Cas, they created a ∆pshX strain and found that PshX functions as a low-energy antenna subunit in energy transfer.
Method
Plasmid pPB1258 was modified to include a kanamycin resistance cassette and variants pPB1322 and pPB1384 were created using Golden Gate assembly to target pshX with CRISPR. Helper plasmids pPB191 and pGO1717 were designed to facilitate these plasmids' transfer.
Results
The pshX gene, found across various Heliobacteriaceae species, suggests an ancient, conserved role, emphasizing the need for further study on its function and distribution in heliobacterial genomes.
Delve into the researchers' findings.
Successful Linux Cluster Institute Hosted by ASU Research Computing
ASU Research Computing hosted its first collaborative training event with the Linux Cluster Institute offering introductory level training at our SkySong facility on February 5 - 9, 2024. The Research Computing team presented technical course material while sharing knowledge and best practices during a close-knit, hands-on networking event with attendees from over 30 other universities and organizations!
What is LCI? The Linux Clusters Institute (LCI) provides education and advanced technical training for the deployment and use of computing clusters to the high performance computing (HPC) community worldwide. Founded in 1998, it includes some of the world’s foremost specialists in building and deploying clustered high-performance computing systems. LCI is the premier international forum to share information on management, administration, and advanced computing techniques for high performance computing.
Why does this event matter? This is the first LCI workshop to be hosted at ASU. With over 30 universities and organizations in attendance, this event was a huge success to not only our local high-performance computing community, but to our communities and networks worldwide. The materials from this workshop were also presented by ASU HPC System Administrators, William Dizon and Alan Chapman.
Which Universities or Organizations were in attendance?
Arkansas Children's Hospital
BioFrontiers Institute - University of Colorado at Boulder
Cal Poly Pomona
California State University, Fullerton
Clark Atlanta University
Converge Technology Solutions
Data In Science Technologies
East Carolina University
Guidehouse (NIH/NHLBI)
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Mississippi State University HPC²
Missouri State University
Morgan State University
University of Missouri - Columbia
Naval Postgraduate School National Center for Atmospheric Research
North Carolina A&T State University
Nova Southeastern University Florida
Naval Surface Warfare Center Carderock Division
Purdue University
Saint Louis University
San Diego State University
SchedMD
Texas A&M University
The MITRE Corporation
University of California Santa Cruz
University of Illinois
University of Minnesota
University of South Florida
US Geological Survey
Washington University School of Medicine
Core Facilities News - March 2024 - METAL Staff Highlight


Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.
Metals, Environmental and Terrestrial Analytical Laboratory (METAL) Core
For this month's newsletter, we're going to focus on the people that make our METAL Core, one of our Materials Characterization and Synthesis facilities, so great!
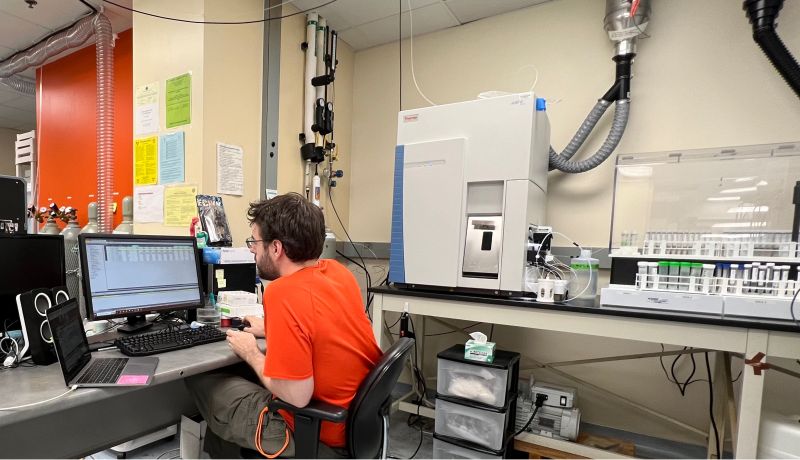

Meet the METAL team

Dr. Gordon specializes in mass-dependent and radiogenic isotopes, with extensive expertise in ICP-MS, MC-ICP-MS and IRMS.
She has been dedicated to elevating ASU as a forefront institution for forensic science research. Collaborating across various disciplines and ASU campuses, she helped establish the Forensic Science Initiative.
This initiative facilitates collaboration between academic researchers and forensic practitioners to address societal needs through research guided by ASU's extensive expertise in science, technology, law and social science.


"No two days are quite the same and METAL gets to work with researchers across many fields and from all around the globe." - Tyler Goepfert
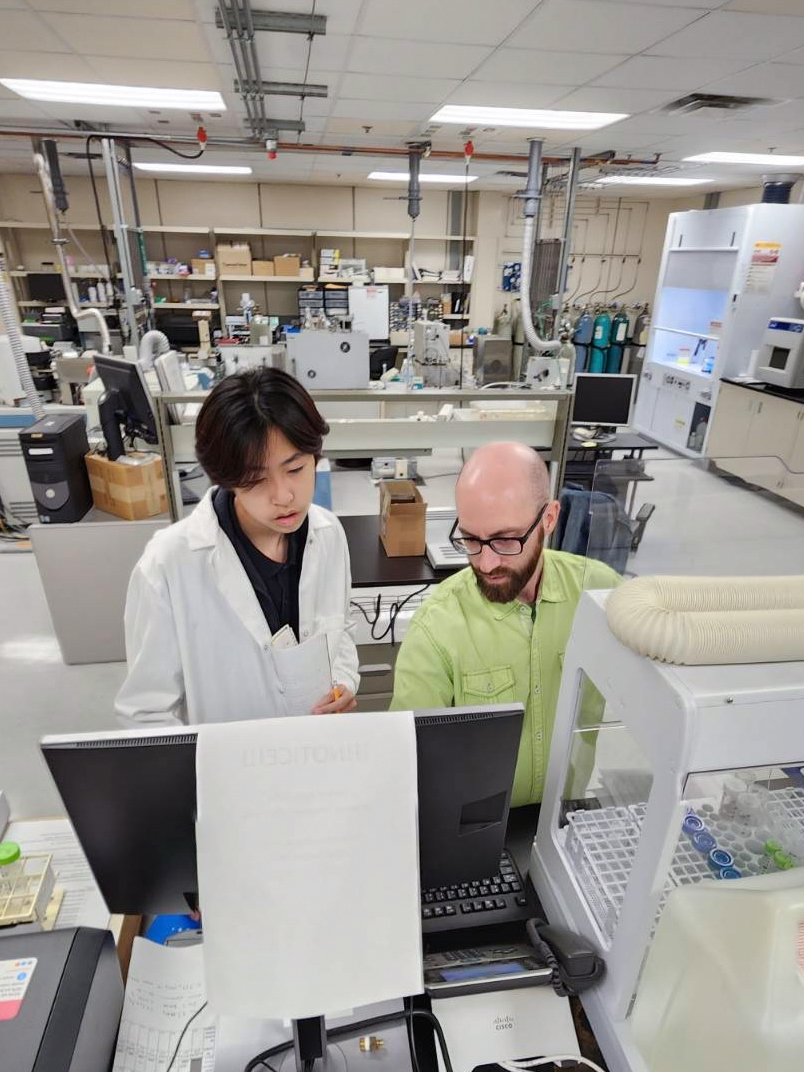


Tyler trained in Germany on one of the earliest commercially available multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometers (MC-ICP-MS), the VG Axiom.
Now more than a decade later, Tyler is still going strong with the great fortune here at ASU to start working with the most state-of-the-art multi-collector on the market, the recently installed Neoma MC-ICP-MS. With METAL's resources, he can work together with students, staff, industry and other guests to quantify even the most subtle of isotope signatures out there.
METAL has the infrastructure to process just about any material and evaluate the isotope composition to probe nearly infinite questions about the world and indeed the universe around us! With many established methods and continuously expanding new methods, our only limit to what we can do is the hours in the day.
METAL Equipment Highlights
Elemental Scientific PrepFAST MC |
Thermo Scientific Quadrupole ICP-MS |
More METAL Core equipment videos.
News
METAL's resources support education
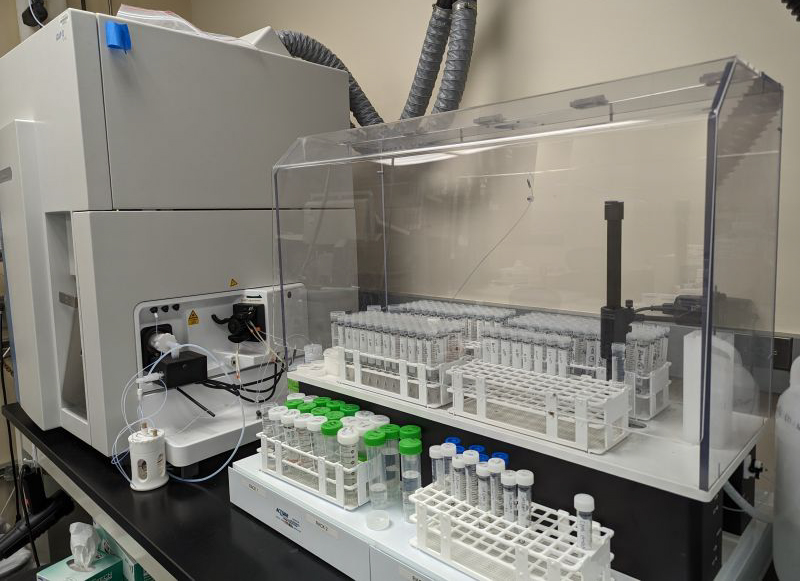
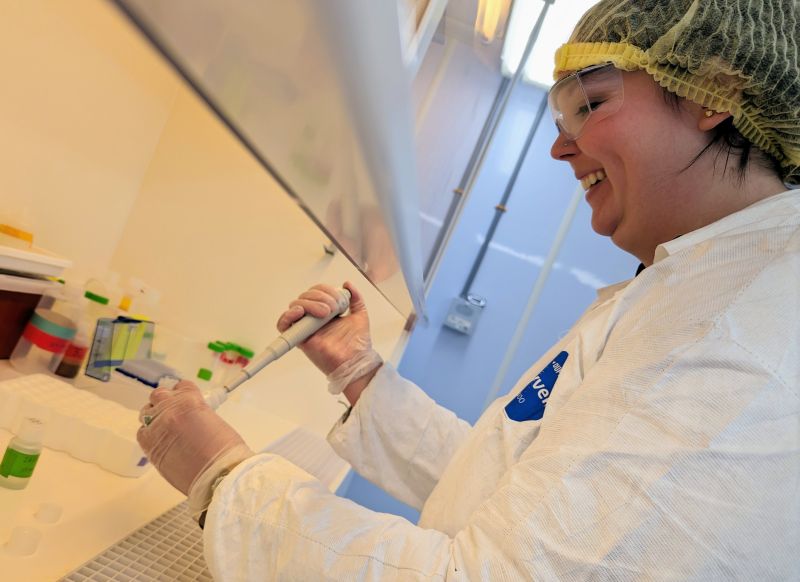


Jenna Watson from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, made a visit to METAL to process samples for her doctoral dissertation. Jenna's research focuses on utilizing stable isotope analysis to investigate dietary composition and geographic mobility among human groups from late medieval Romania.
During her visit, Jenna utilized METAL facilities including our trace clean laboratory and our ICP-MS technology. She also employed our Prepfast equipment for sample preparation. Excitingly, Jenna's strontium isotope samples will be among the first to be analyzed using our new Thermo Fisher Neoma MC-ICP-MS, showcasing the cutting-edge capabilities of our research facilities.
Announcing ASU SolarSPELL's new design!
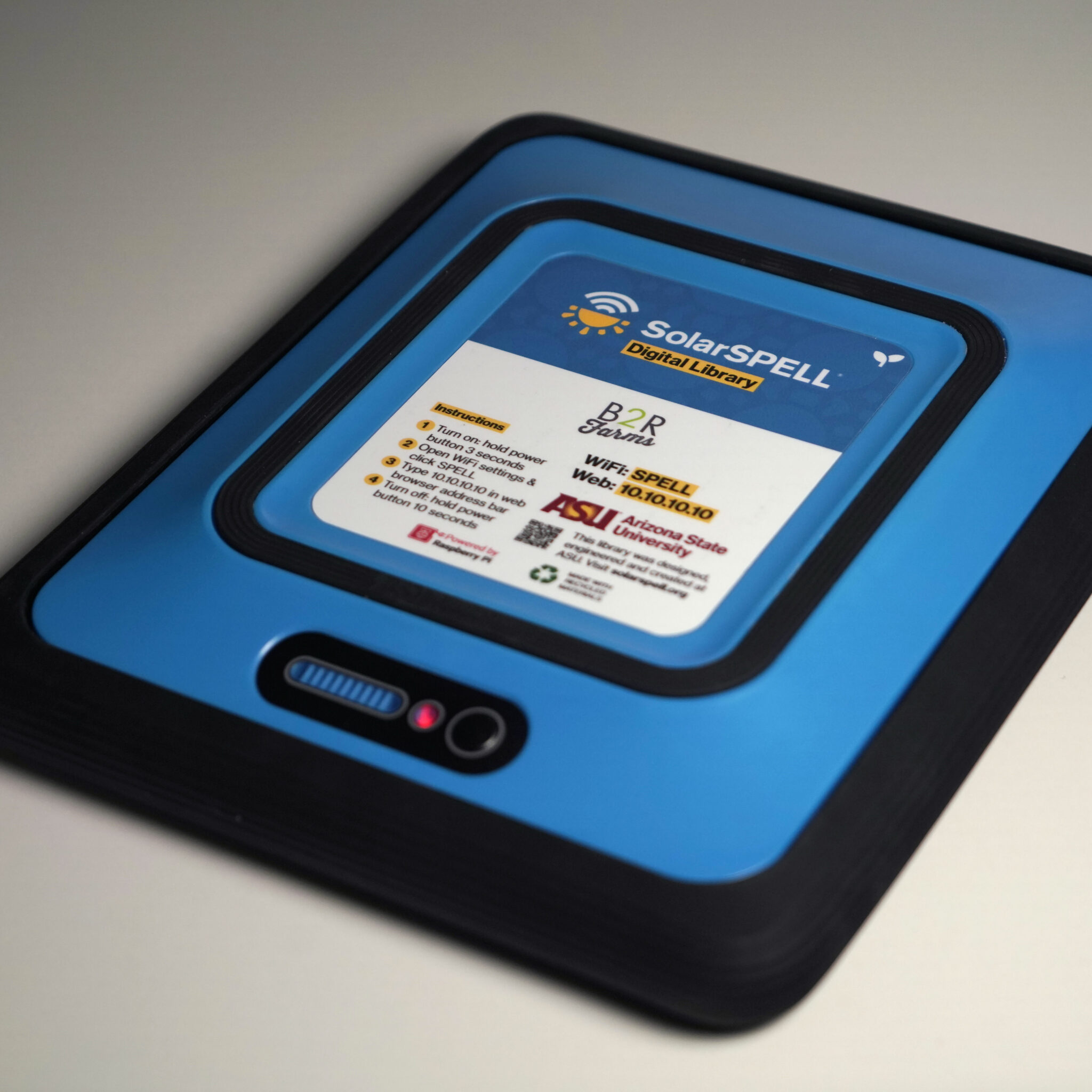
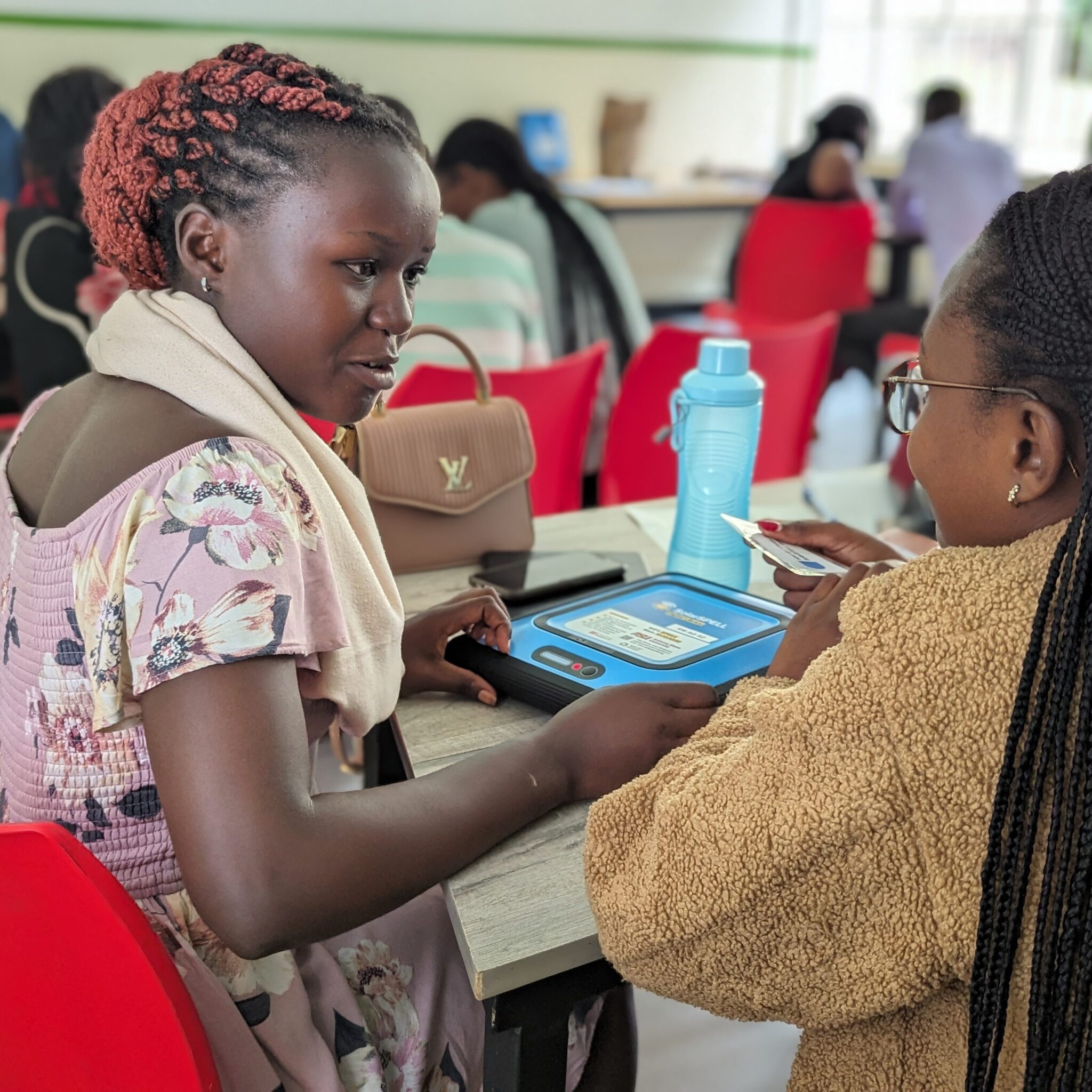


ASU SolarSPELL has introduced a revamped design for its digital libraries, created with input from ASU's students, faculty and staff - including that of our Instrument Design and Fabrication Core. The updated design features a smaller, more robust case made from recycled plastic, enhancing its durability. Its innovative, patent-pending charge controller harnesses solar power and connects to an offline web platform, improving the overall utility and educational impact of the libraries.
These enhanced SolarSPELL libraries are already benefiting communities in Rwanda and the Hopi Tribe in Arizona. In Rwanda, they aid agricultural education alongside B2R Farms, and in Arizona, they provide essential health education to the Hopi Tribe. This reflects SolarSPELL's dedication to delivering educational resources to remote and underserved regions, using technology to support community empowerment and sustainable growth.
More about SolarSPELL's new hardware design.
How the SolarSPELL is changing the world.
Publications
Trace element concentration as proxies for diagenetic alteration in the African archaeofaunal record: Implications for isotope analysis
This research used METAL's recently retired Thermo Scientific Neptune and gives a preview of what is possible with our Neoma MC-ICP-MS, which has recently been installed.
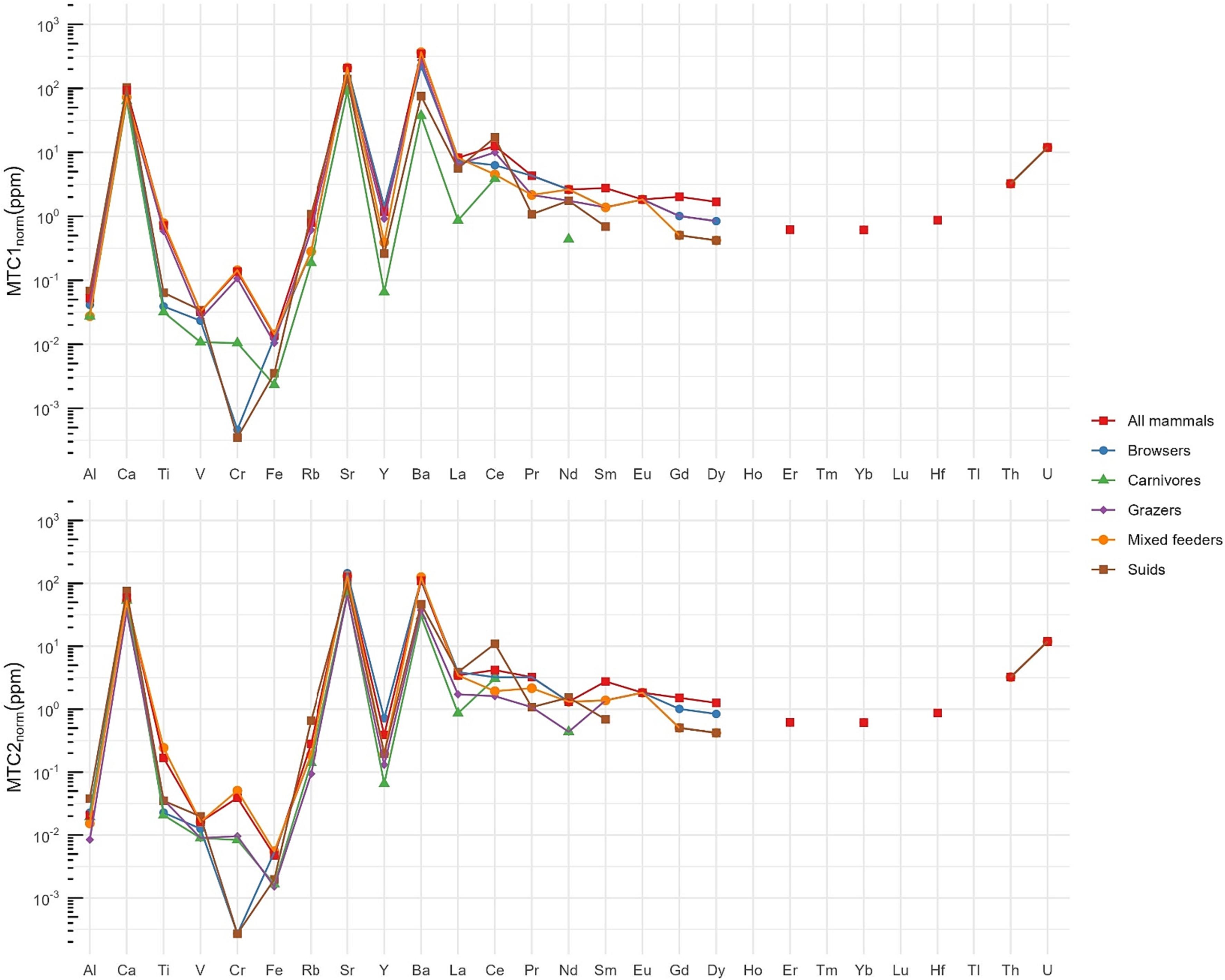
Abstract
Isotope ratio analyses of hard tissues like tooth enamel and ostrich eggshell (OES) inform mobility and paleoecology. Researchers enhanced the Maximum Threshold Concentrations (MTCs) method to screen for diagenesis, introducing a new metric (MTR) of 85Rb/88Sr.
Method
The research measured elemental concentrations in modern ostrich eggshell (OES) and Rb/Sr ratios by LA-MC-ICP-MS in the same samples, followed by the calculation of maximum threshold concentrations and ratios.
Results
Trace element concentrations vary by specimen origin, emphasizing the need for locality-specific reference sets for OES. The research proposed a cutoff of around 10e1 ΣREE for unaltered samples, especially when uranium levels are low. Additionally, typical MTR around 10e−4 indicate unaltered enamel and OES.
Delve into the researchers' findings.

